VCP (Valosin Containing Protein) Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 18, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
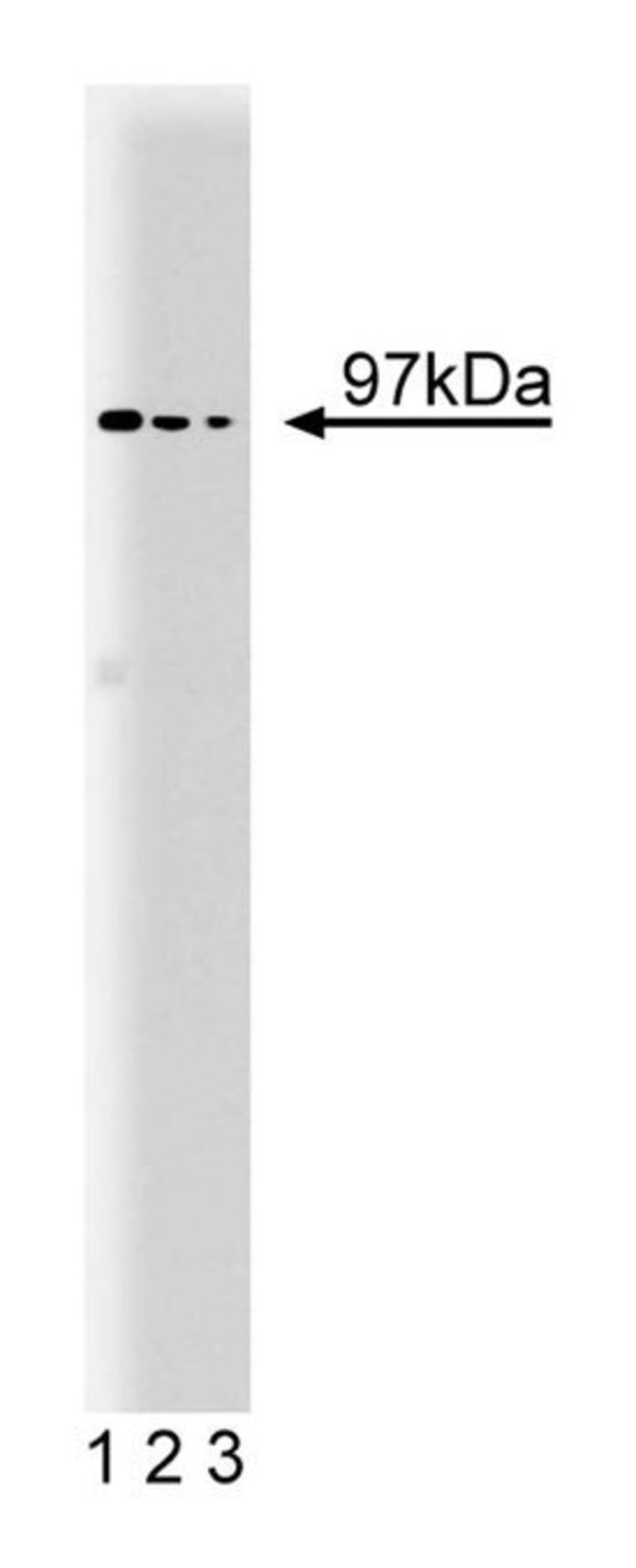
ATPases that belong to the ATPase associated with different cellular activities (AAA) family are homo-oligomeric proteins that have roles in cell cycle regulation, protein degradation, organelle biogenesis, and vesicle mediated-protein transport. Valosin containing protein (VCP) is a AAA family member that is found as a hexamer in rat liver. In vitro, VCP catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP, but this activity is distinct from classical transport ATPases. VCP protein is found primarily in the transitional elements between the rough and smooth ER (TER), but stimulation with EGF leads to VCP translocation to the nucleus. Antibodies to VCP can perturb cell-free formation of transition vesicles from isolated TER of rat liver, and can inhibit transfer of material from ER to Golgi in a reconstituted membrane system. VCP is phosphorylated after T-cell activation, and PTPH1 dephosphorylation of VCP correlates with suppression of cell growth. In addition, the N-terminal region of VCP binds to the DNA damage repair protein, BRCA1. Thus, VCP may have roles in both ER protein transport and nuclear function, which are important for cell growth and survival.Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135526 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 612183 |