SNAP-25 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 20, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
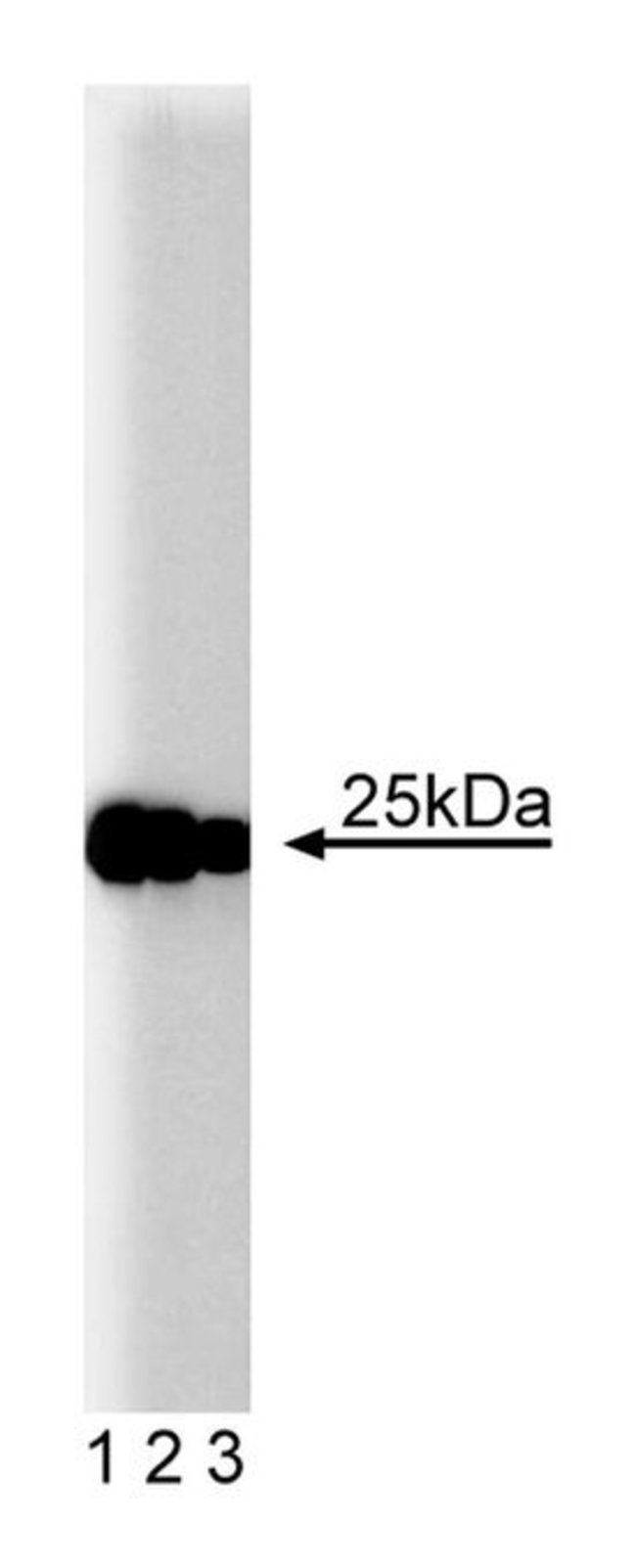
Release of neurotransmitters from neurons is regulated by exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. This exocytosis is mediated by a complex consisting of membrane components of both the synaptic vesicle and the synaptic plasma membrane. The fusion complex consists of the soluble NSF (N-ethyl-maleimide-sensitive factor) and SNAPs (soluble NSF attachment proteins), along with the receptor proteins (known as SNAREs) synaptobrevin, synaptotagmin, syntaxin, and SNAP-25 (synaptosomal-associated protein of 25kDa- the name is coincidental to the previously mentioned “SNAP” terminology). SNAP-25 and syntaxin are plasmalemmal proteins (designated as t-SNAREs) while synaptobrevin and synaptotagmin are vesicular proteins (designated as v-SNAREs). These four proteins are thought to constitute an initial SNARE docking complex for regulated exocytosis. SNAP-25 lacks a transmembrane domain, but is linked to the membrane by palmitoylated cysteine residues in the central region of the molecule.Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134926 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610366 |