mGluR1 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 20, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
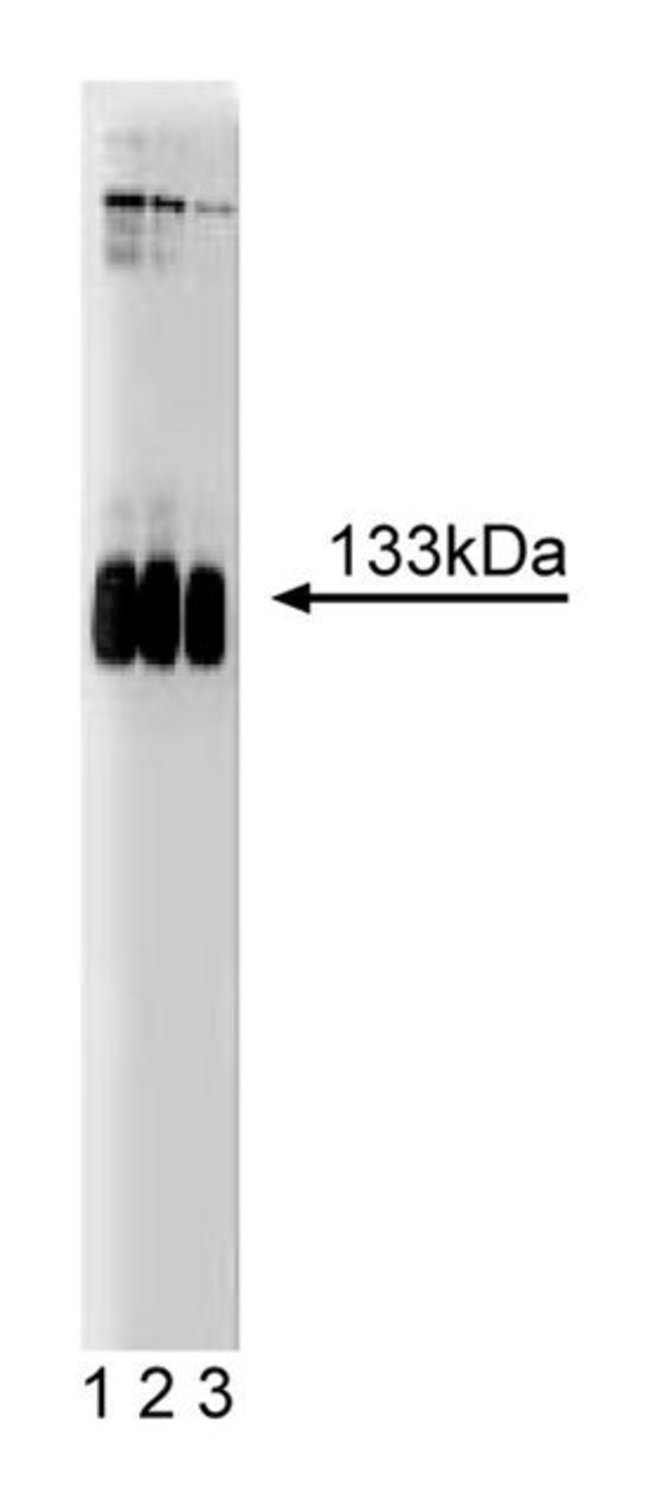
Glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter and functions in multiple roles in the CNS. The functional diversity of glutamate is exemplified by two distinct groups of glutamate receptors: ionotropic and metabotropic. Coupling with G proteins provides the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) with the capacity for intracellular signal transduction. Eight metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1-8) and several Ca2 sensing receptors belong to a novel G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. The mGluRs possess the seven putative transmembrane domains which are characteristic of GPCR proteins. However, they exhibit no additional sequence homology to any member of other GPCR families. mGluR1 has large hydrophilic sequences in both the N- and C-terminal sides of the seven transmembrane domains. The sizable extracellular N-terminal domain is homologous to bacterial periplasmic binding proteins and serves as the glutamate binding site. mGluR1 activates phospholipase C (PLC), resulting in phosphoinositide turnover and, in turn, Ca2 ; mobilization necessary for many signal transduction events.Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135213 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610964 |