iNOS/NOS Type II Mouse anti-Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 6, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
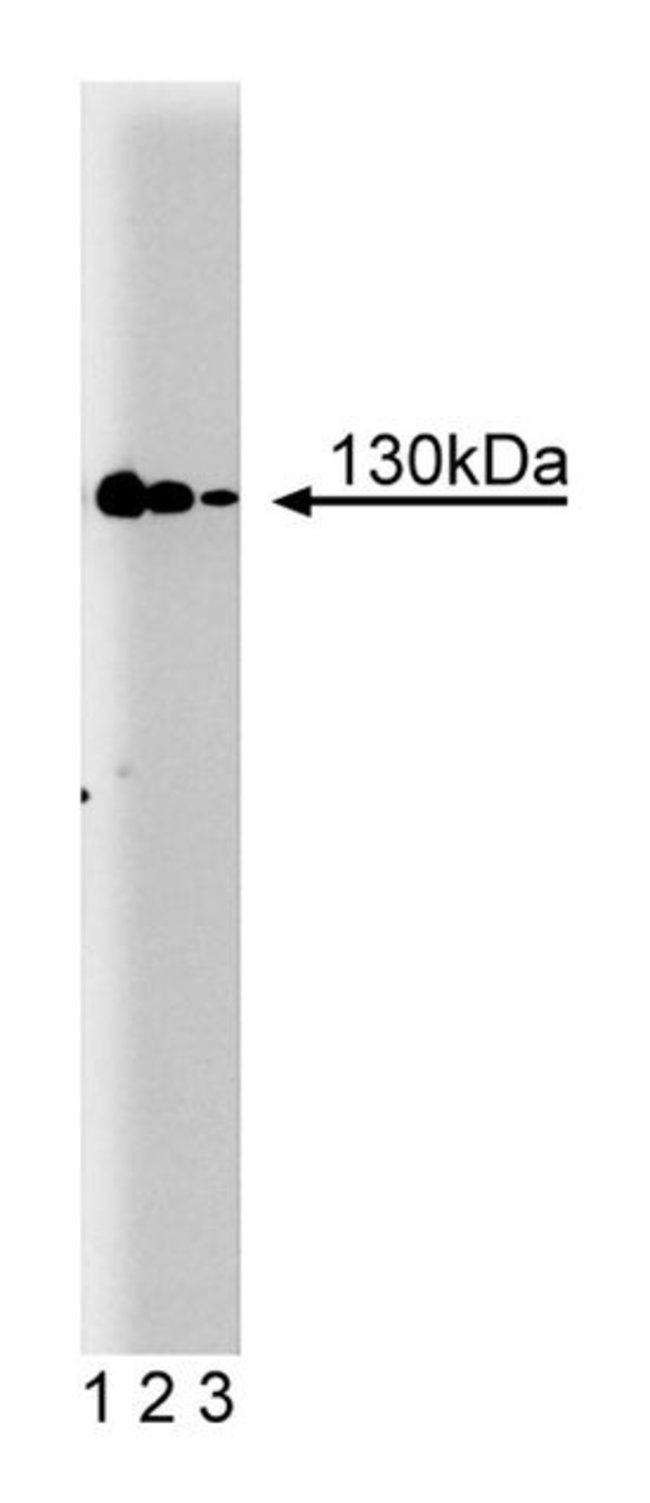
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS), a cell-type specific enzyme, catalyzes the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a short-lived radical that transmits cellular signals involved in vasorelaxation, neurotransmission, and cytotoxicity. In macrophages and other cell types, NOS (iNOS or macNOS) activity increases following exposure to cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-1) and microbial products (lipopolysaccharide (LPS)), iNOS is activated independently of Ca2 /calmodulin and its level of expression is tightly controlled by several transcription factors, including NFκB. Data indicates that TGF-β affects translation of iNOS mRNA and decreases iNOS protein stability. Normally undetectable in brain tissue, iNOS mRNA has been observed in CNS tissues of animals under experimental pathologic conditions. iNOS and nNOS share 51% amino acid homology with the greatest degree of divergence in the calmodulin binding domain.Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134913 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610329 |