Hic5 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 34, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
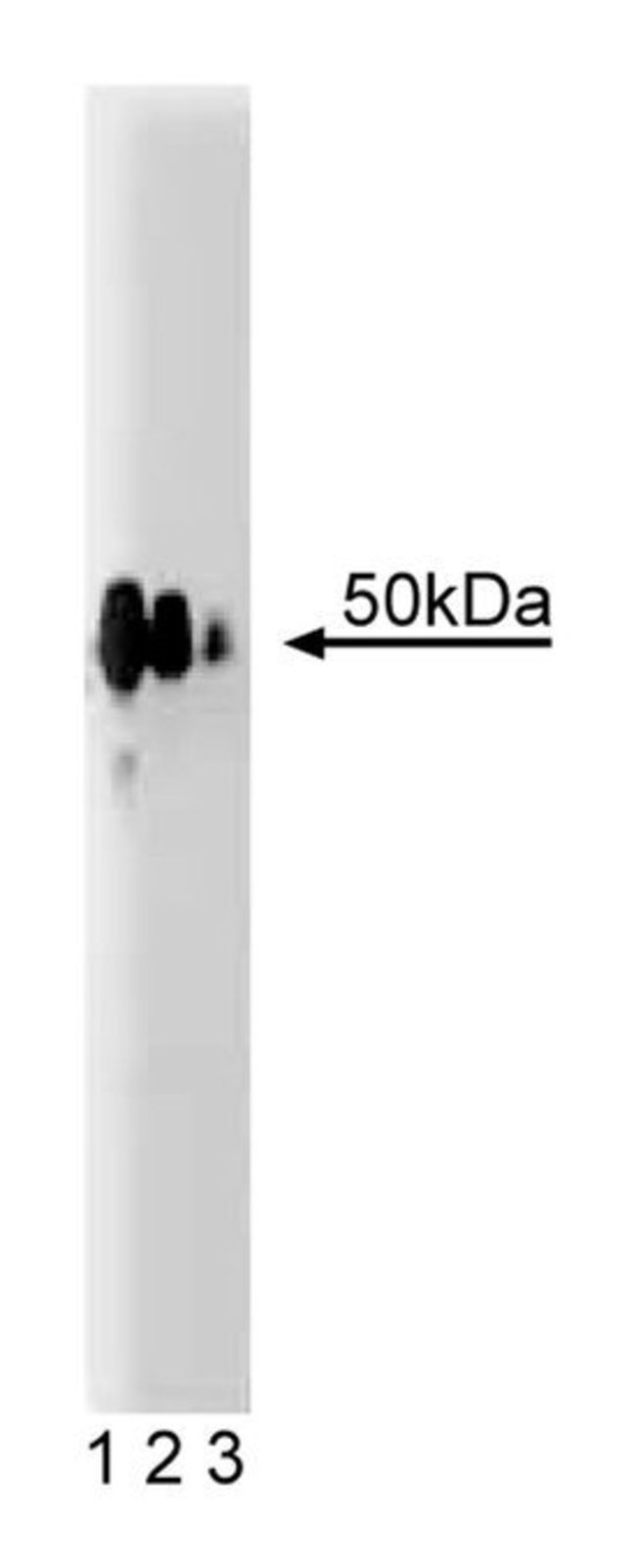
Focal adhesions are cell structures terminal to the actin-stress fiber bundles. They attach cultured cells to their substratum or extracellular matrix. These adhesions occur through the integrin receptor molecules which link cytoskeletal proteins and extracellular matrix. The intracellular adhesion is composed of a number of proteins such as paxillin, VASP, vinculin, and the focal-adhesion kinases FAK and PYK2/CAKβ. Hic-5, also described as hydrogen peroxide inducible-mRNA, is a focal adhesion protein that binds to FAK and PYK2. It is ubiquitously expressed with the highest levels found in lung, spleen, and heart. Induction of Hic-5 is accomplished by hydrogen peroxide or TGFβ1 and is repressed in K-ras transformed cells. Like paxillin, Hic-5 is tyrosine phosphorylated in Src-transformed cells and is highly similar to paxillin in its primary structure. Both proteins contain LIM domains and LD motifs. In addition, Hic-5 localizes to focal adhesions and co-immunoprecipitates with PYK2/CAKβ in vivo. Thus, Hic-5 may be a substrate for CAKβ and play a role in signal transduction during proliferation, cell motility, and adhesion.Host Species: MouseClone: 34Isotype: IgG1Species Reactivity: RatImmunogen: Mouse Hic-5 aa. 73-186Formula Weight [Chemical]: 50kDaImmunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135298 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 611165 |