DAP Kinase Mouse anti-Human, Unlabeled, Clone: 17, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
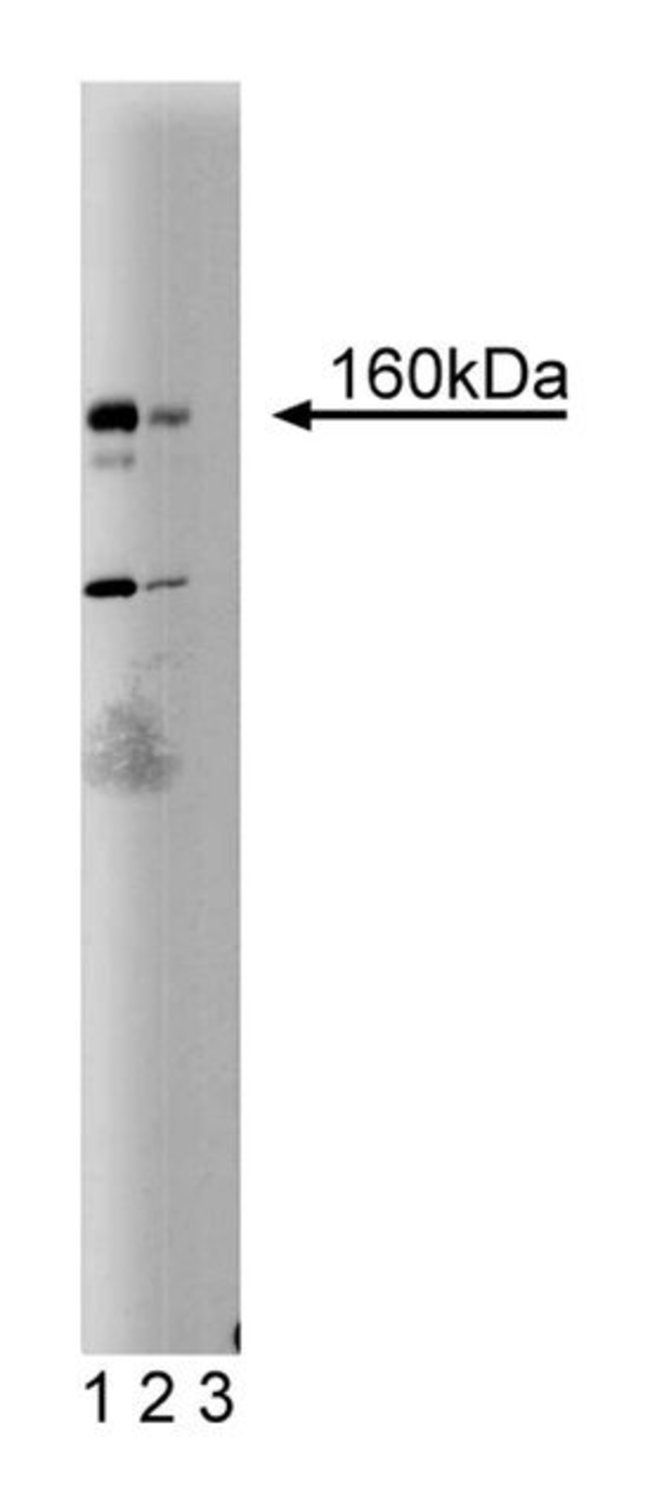
Chronic exposure to extracellular signals such as interferons induce the inhibition of cell proliferation followed by cell death. The gene for DAP Kinase (Death Associated Protein Kinase) was identified using a novel approach named Technical Knockout. Briefly, Hela cells were transfected with an antisense cDNA expression library, then exposed to Interferon-γ. The surviving cells, with their antisense cDNAs, were rescued and the “protecting” genes isolated. The DAP Kinase gene encodes a protein of 1423 amino acids, a molecular weight of 160kDa, a kinase domain at its amino terminal region, ankyrin repeats in the middle region, and a death domain at the extreme C-terminus. DAP Kinase phosphorylates at Ser/Thr residues in a Ca2 /Calmodulin-dependent fashion. It has been demonstrated that Ca2 /Calmodulin binds directly to DAP Kinase at its amino terminal region. In addition, immunostaining studies localized DAP Kinase in association with the actin filaments where it may phosphorylate myosin light chain. Thus, this novel cytoskeletal and Ca2 /Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase plays a role in interferon-γ-induced cell death.Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134897 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610291 |