CTCF Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 48, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
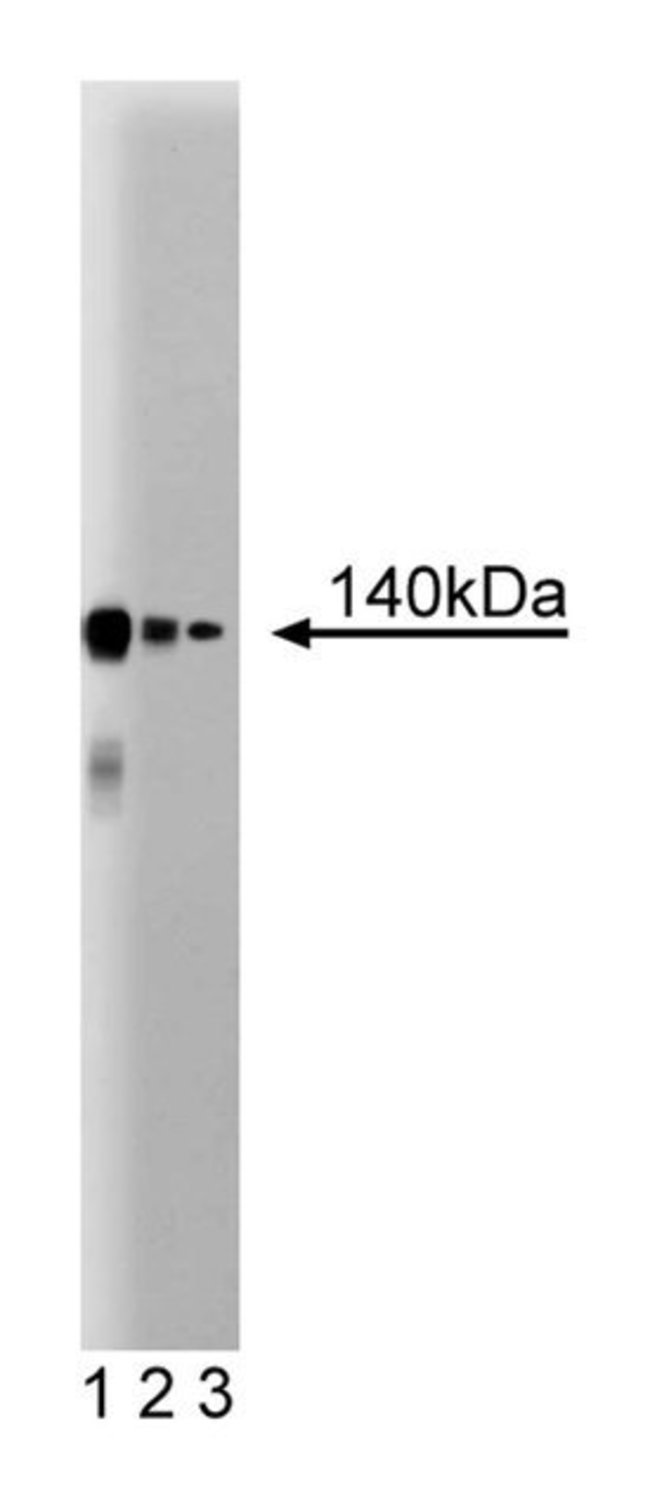
The family of nucleic acid-binding C2H2 type zinc finger transcription factors is divided into two classes. One class consists of small proteins (Gli1, Krox-20, WT1, Egr-1, and Sp1) with conserved zinc finger clusters of 3 to 5 units, while the other class (ZNF91, ZNF74, ZFP37, CTCF) can contain more than 10 zinc finger clusters. CTCF is a ubiquitously expressed, highly conserved transcription factor that contains 10 C2H2- and 1 C2H-type zinc-finger motifs. CTCF binds to and represses transcription at the promoter-proximal regions of c-myc oncogenes, while CTCF can bind to and activate transcription at the promoter for amyloid β. Another mechanism of CTCF-mediated repression may include binding to insulator regions between enhancers and promoters resulting in enhancer blocking. In addition, CTCF gene may be a candidate tumor suppressor gene, since it localizes to a narrow cancer-associated chromosome region, and has been shown to have tumor-specific rearrangements in breast cancer patients. Thus, CTCF transcriptional regulation may be important for cell cycle progression, differentiation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis.Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135510 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 612149 |