Caspase-3/CPP32 Mouse anti-Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 46, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
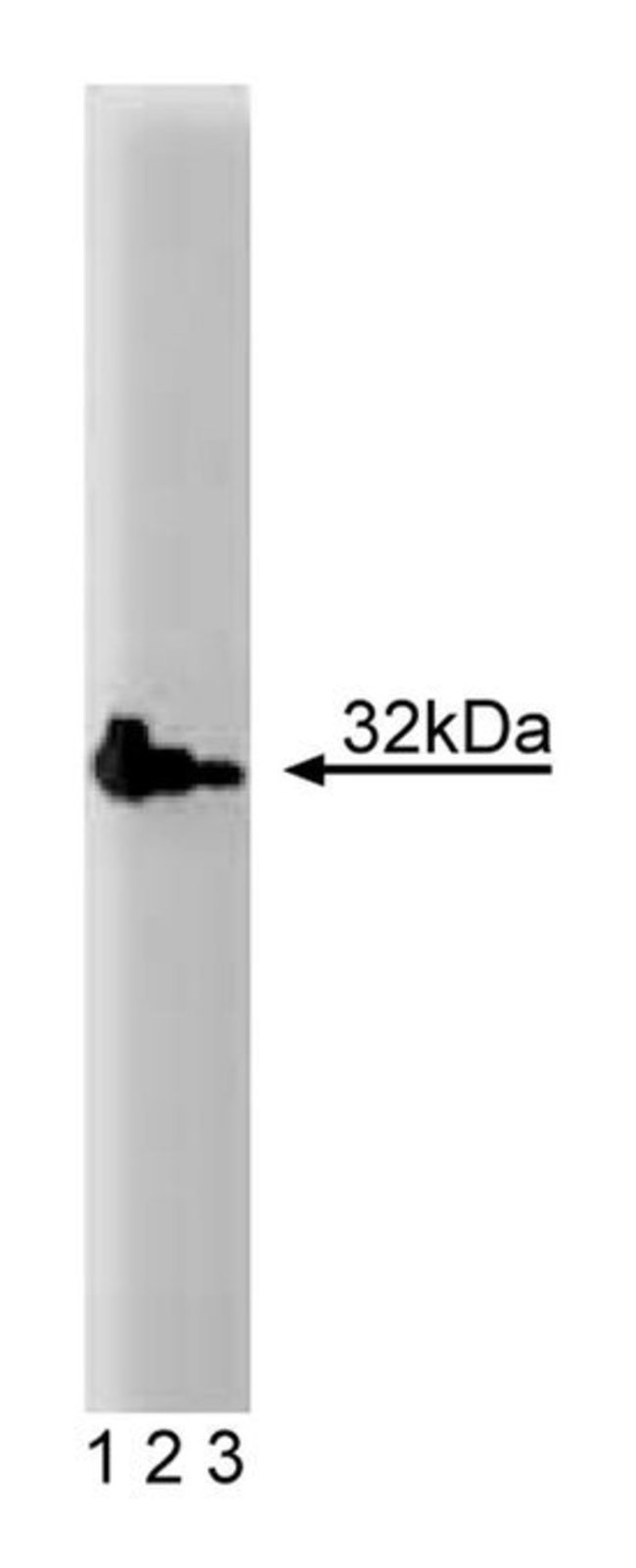
Apoptosis, a selective process of genetically programmed cell death, occurs during normal cellular differentiation and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptotic cells are characterized by loss of cell volume, plasma membrane blebbing, nuclear condensation, chromatin aggregation, and endonucleocytic degradation of DNA into nucleosomal fragments. Caspase-3 (CPP32, Yama, apopain) is a member of the family of cysteine proteases which includes interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme (ICE) and C. elegans protein, Ced-3. An apoptotic signal such as granzyme B of cytotoxic T-cells (CTLs) or ICE-like proteases induces the intracellular cleavage of Caspase-3 from the inactive proform (32kDa) to the active form which consists of the p20, p17, and p12 subunits. The active form of Caspase-3 cleaves several other apoptotic proteins including proteins such as DNA fragmentation factor (DFF). Apoptosis can be inhibited by coexpression of Bcl-2 as well as inhibitors of Caspase-3 or other members of the family of cysteine proteases. This antibody recognizes the mouse 32kDa pro-Caspase-3 and the p17 cleaved form of Caspase 3 in T cell lymphocytes treated with camptothecin.Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135262 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 611049 |