Cadherin-5 Mouse anti-Human, Unlabeled, Clone: 75, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each

Details:
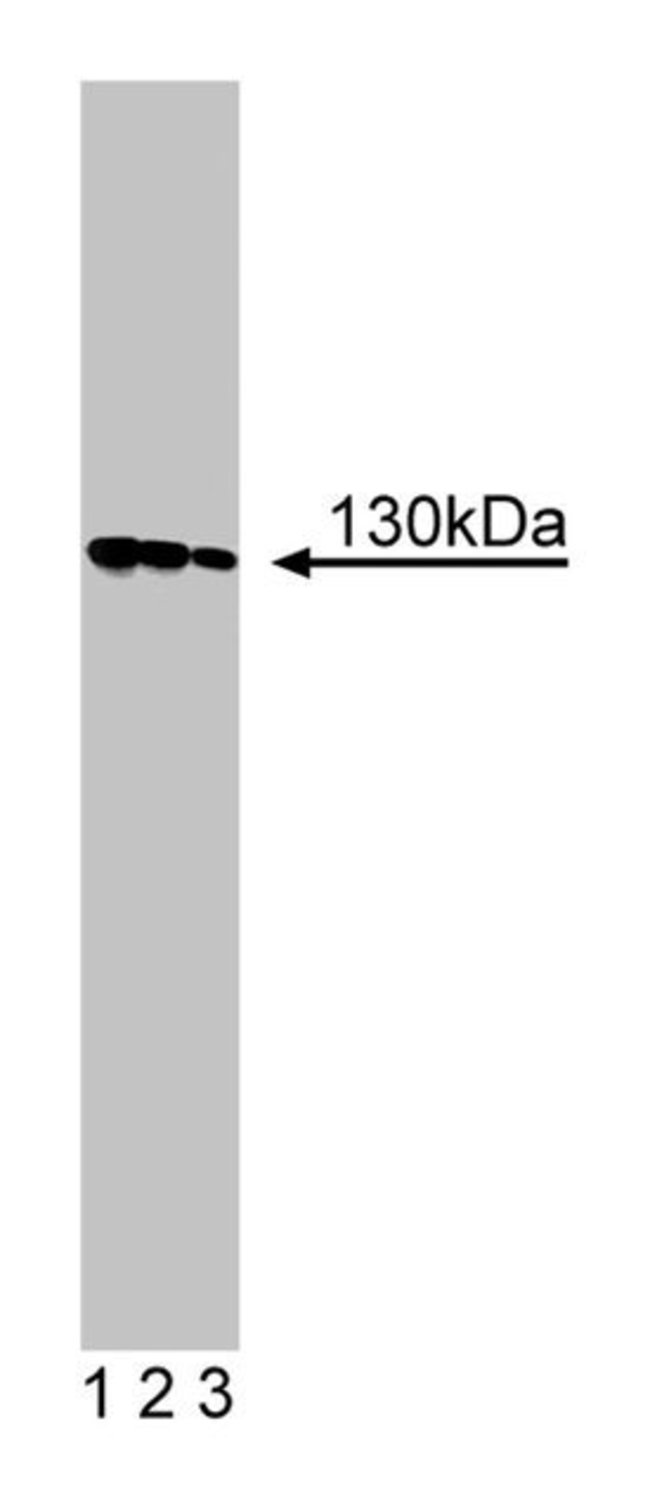
Cadherins are a family of transmembrane glycoproteins involved in the Ca2 - dependent cell-cell adhesion that occurs in many tissues. These proteins are similar in their domain structure (45-74% amino acid conservation), Ca2 and protease-sensitivity, and molecular weight. Cadherin-5 (VE-Cadherin or CD144) is one of a number of cadherins (cadherin-4 through -11) whose cDNAs were isolated from rat brain and retina. These cadherins have a cytoplasmic domain that is highly conserved relative to previously identified cadherins, indicating that this domain is essential for cell adhesion activity. This function is mediated by cadherin interaction with cytoskeletal proteins. However, Cadherin-5's cytoplasmic domain has the lowest degree of homology with the other cadherins. Cadherin-5 is expressed in brain and various other tissues, including umbilical cord vein endothelial cells. A new type of adhering junction has been identified in certain vascular endothelial cells. These junctions are known as “complexus adherens” and are morphologically and compositionally distinct from desmosomes and zonula adherens junctions. The complexus adherens of endothelial cells lack desmosomal cadherins as well as E-Cadherin. However, these cells are rich in Cadherin-5 which colocalizes with desmoplakin and γ-Catenin (plakoglobin).Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134871 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610252 |